The idea for this blog post all started when I was in the car with my 4-year-old twins and asking them what they wanted in their premade dinner snack box because we had swimming lessons that night so I like to give them a little pre-dinner meal in the car so they can make it until actual dinner after swimming lessons.
First, I asked one twin and he told me what he wanted. I then moved on to the other twin asking him what he wanted to eat, however, he was fully engulfed in play in his car seat and didn’t hear my question. I then proceeded to say, “Earth to Boden”. Both boys thought that was such a weird comment to make. Was I trying to send Boden to earth? But he was already on earth…right?
I then went on to explain that it is an expression meaning, “Hello, are you paying attention?” They both laughed and said, “oh!”
This sweet little moment with my boys got me thinking about idioms and just how confusing they can be. So I decided I’d bring to you a quick guide to idioms and figurative language as well as 10 common examples with a free idiom activity for your child or students.

Idioms and Figurative Language: A Comprehensive Guide
Idioms are figurative expressions that are common in everyday speech in the English language. As a form of figurative language, idioms use words in an imaginative manner to convey non-literal meanings that are not immediately obvious from the literal interpretation of the words.
Understanding figurative language is important for effective communication in English, as it can convey complex ideas and emotions in a concise and memorable way. Idiomatic expressions are just one type of figurative language, but they are common and can be found in many different contexts, from everyday conversations to literature.
Enhancing figurative language skills can be challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of the English language and the ability to use words creatively.
However, by learning about the different types of figurative language and practicing their use in everyday conversations, you can help your students become more confident and effective in their communication!
We have gathered 10 common idiom videos and have created a fun free activity to go along with them below.
Key Takeaways
- Idioms are a form of figurative language that use words in an imaginative manner to convey a meaning that is not immediately obvious from the literal interpretation of the words.
- Figurative language is important for effective communication in English, as it can convey complex ideas and emotions in a concise and memorable way.
- Enhancing your figurative language skills can be challenging, but by learning about the different types of figurative language and practicing their use in everyday conversations, you can become more confident and effective in your communication.

Understanding Figurative Language
Figurative language is the use of words or expressions that convey a non-literal meaning, often to create a more vivid or impactful image in the mind of the listener or reader.
It goes beyond its literal meaning to convey a more abstract or symbolic idea.
This can include the use of metaphors, similes, idioms, and other types of figurative expressions.
Distinguishing Literal from Figurative
- Literal Expressions – the straightforward, dictionary meaning of words or a phrase.
Example: “give a cold shoulder” would mean to actually give some a shoulder that is frozen.
- Figurative Meaning – the listener has to interpret the non-literal meaning based on context, cultural knowledge and personal experiences.
Example: “give a cold shoulder” has different meanings in the English language, and is a type of idiomatic expression that means to purposefully be rude or unfriendly to someone.
Understanding figurative language in everyday speech is an essential aspect of effective communication. It is a powerful tool that allows us to convey complex ideas and emotions in a more engaging and memorable way, and can help to create a deeper connection with the listener or reader.
Types of Figurative Language
There are several types of figurative language that writers use to convey powerful messages in a creative way. These tools of expression are often used to add depth and meaning to the text.
Here are some of the most commonly used types of figurative language!
Similes and Metaphors are used for comparison.
- Simile – Uses “like” or “as” to compare two things that are not alike.
Example: Her eyes are as blue as the sky.
- Metaphors – Directly compares two things without using “like” or “as”.
Example: Life is a journey.
Idioms and Proverbs are used to convey human characteristics and emotions.
- Idiom – A phrase or expression that has a figurative meaning that is different than its literal meaning.
Example – I can put that together it’s a piece of cake.
- Proverb – Is a short saying that is used to convey a moral or lesson.
Example – You can’t teach an old dog new tricks.
Hyperbole and Understatement are opposite figures of speech.
- Hyperbole – Is an exaggeration used to emphasize a point.
Example: I told you a million times.
- Understatement – Downplays the importance of something.
Example: It’s just a scratch.
Personification and Anthropomorphism are two examples of figurative language that give human characteristics to non-human things.
- Personification – Is when a non-human object, animal, or thing is described with human characteristics.
Example: The alarm clock yelled.
- Anthropomorphism – Is when a non-human object, animal, or thing behaves like a human.
Example: The wind whispered through the trees.

Challenges in Figurative Language
Understanding idioms and figurative expressions can be challenging for many individuals, including non-native English speakers and those with language disorders.
For Non-Native Speakers
Non-native English speakers may struggle to understand idioms and figurative language due to the different meanings these expressions can have. Idioms often have non-literal meanings that are not immediately apparent from the words used.
Another challenge for non-native speakers is the cultural understanding or understandings of the origins of the phrase required to grasp the meaning of common idioms.
Idioms are often rooted in cultural references that may not be familiar to those from different backgrounds.
For Individuals with Language Disorders
Individuals with language disorders may also struggle to understand idioms and figurative language. These individuals may have difficulty processing the metaphorical meanings of idioms and may interpret them literally.
For example, someone with a language disorder may interpret the idiom “hold your horses” as a literal instruction to hold onto a horse.
Another challenge for individuals with language disorders is the difficulty in understanding the context in which idioms are used. Idioms often rely on context to convey their meaning, and individuals with language disorders may have difficulty understanding this context.
For example, the idiom “the cat’s out of the bag” means that a secret has been revealed, but this meaning may not be clear to someone who is not familiar with the situation in which the idiom is used.
SEE ALSO: 31 Best Wordless Videos to Teach Problem Solving
Idioms in the English Language
Idioms are a type of figurative language that native English speakers use every day. They are phrases that have a meaning different from the literal interpretation of the words. Idiomatic expressions are an essential part of the English language, and they add color and depth to everyday conversation.
Common Idioms and Their Meanings
English has a vast collection of idiomatic expressions that are used every day by native speakers. Each idiom has its meaning, and it is essential to understand the context in which it is used to comprehend its meaning.
Origins and Evolution
Idioms have been a part of the English language for centuries, and their origins can be traced back to cultural metaphors. Many idioms have their roots in literature, mythology, and historical events.
For example, the idiom “barking up the wrong tree” has its origins in hunting, where dogs would bark up the wrong tree, indicating that they were chasing the wrong prey. Over time, the meaning of idioms can change, and new idioms can emerge.
Regional Variations
Idioms can vary from region to region, and even from country to country. For example, the idiom “take a rain check” is commonly used in North America to mean that someone cannot accept an invitation but would like to do so at a later time.
In the UK, the equivalent idiom is “take a ticket for the next bus.” Understanding regional variations in idiomatic expressions can help non-native speakers communicate more effectively with native speakers.
SEE ALSO: 71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Scenarios

Enhancing Figurative Language Skills
To improve our figurative language skills, we need to learn and practice strategies that can help us understand and use idioms in our daily communication.
Learning and Practice Strategies
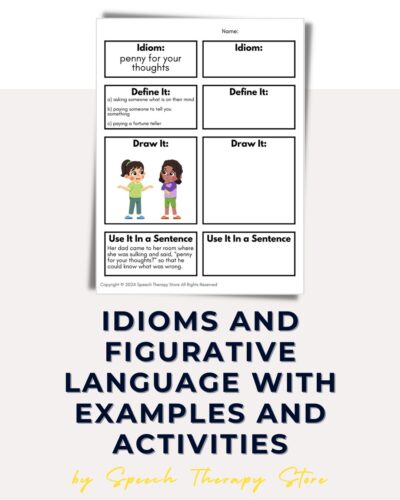
One of the best ways to learn idioms is through practice exercises. Below we have created a free idiom activity that can help your students learn and understand the meaning of idioms. Other exercises can be in the form of quizzes, games, or worksheets, and can be a fun way to learn new idioms.
Another great way to practice idioms is through video examples, which we have compiled below.
A great way to enhance our figurative language skills is by using context clues. Context clues are the words or phrases surrounding an unfamiliar idiom that can help us understand its meaning. By analyzing the context, we can decipher the meaning of the idiom and use it in our communication.
Contextual Understanding and Usage
To use idioms effectively, we need to understand the meaning of the words that make up the idiom. By understanding the word meanings, we can use idioms in the right context and convey our message effectively. We can also group idioms together based on their meaning and use them in social groups.
SEE ALSO: Problem Solving Wheel: Help Kids Solve Their Own Problems

10 Common Idiom Examples with Video Explanations
We have compiled 10 idiomatic expressions that are common in the english language. Use the one minute short videos, by @TomsTalkingELA, as a way to explain these figurative expressions in further detail.
These videos are powerful tools to explain the meaning of words, the origins of the phrase, the idioms non-literal meanings, and examples of how to use these common idioms in everyday speech.
Don’t forget to download our free common idiom exercise activity below!
Breaking the Ice

Back to the Drawing Board

To Be All Ears

Cutting Corners

Eating your Words

Under the Weather

Judge a Book by its Cover

Crying over Spilled Milk

Break a Leg

Penny for your Thoughts

Conclusion
Idioms and figurative expressions can be challenging but are an effective way to communicate with peers and in different social groups.
We hope this quick explanation, as well as videos and activities to teach commonly used idioms, was helpful for you! Be sure to grab the 10 Commonly Used Idioms Activity. This is a free preview of our 100 Common Idioms + Quizzes Bundle!
Grab Your Free 10 Commonly Used Idioms Activity Here!
Simply enter your name and email to have this free 10 Idiom Activity emailed directly to your inbox!
Buy the Complete 100 Commonly Used Idioms Activity Here!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are examples of idioms and their meanings?
Idioms are expressions that convey a figurative meaning different from the literal meaning of the words used. Examples of idioms and their meanings include “kick the bucket” which means to die, “at the drop of a hat” which means to do something right away, “break a leg” which means good luck, “raining cats and dogs” which means heavy rain.
How does figurative language enhance communication?
Figurative language enhances communication by adding depth, color, and creativity to speech and writing. It helps convey emotions, experiences, and ideas in a way that is more interesting, memorable, and engaging than literal language. Figurative language can also help build rapport, establish trust, and create a sense of connection between the speaker and the listener.
Can you list different types of figurative language with definitions?
There are many types of figurative language, including:
- Simile: A comparison between two unlike things using “like” or “as.” Example: “She sings like an angel.”
- Metaphor: A comparison between two unlike things without using “like” or “as.” Example: “Life is a journey.”
- Personification: Giving human qualities to non-human things. Example: “The wind whispered in my ear.”
- Hyperbole: Exaggerating for effect. Example: “I’ve told you a million times.”
- Alliteration: Repeating the same sound at the beginning of words. Example: “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.”
What distinguishes literal from figurative language?
Literal language refers to the use of words in their usual or most basic sense, while figurative language refers to the use of words in a non-literal or imaginative way. Literal language is straightforward and factual, while figurative language is more expressive, creative, and subjective.
How can figurative language be effectively used in speech therapy?
Figurative language can be effectively used in speech therapy to help clients improve their language skills, especially in areas such as vocabulary, comprehension, and social communication. By teaching clients to identify and use figurative language, speech therapists can help them become more effective communicators and better able to navigate social situations.
What role does alliteration play in figurative language?
Alliteration is a type of figurative language that involves the repetition of the same sound at the beginning of words. It is often used in poetry, slogans, and advertising to create a memorable and catchy effect. Alliteration can also be used to emphasize certain words or ideas, and to create a sense of rhythm and flow in speech and writing.
Want Even More Lesson Plans for Speech Therapy?
- Free SLP Planner [Updated Yearly]
- 917+ Best Free Boom Cards for Speech Therapy
- 31 Best Wordless Videos to Teach Problem Solving
- 133+ Categories List for Speech Therapy
- The Best Handout for Phonological Processing Disorder Therapy
Want the Best of the Bests?
Be sure to check out our most popular posts below!
- 21 Best Reinforcement Games for Speech Therapy / Teletherapy
- Best IEP Resources
- 71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Scenarios
- 430+ Free Multisyllabic Words List Activity Bundle
- 432+ Free Measurable IEP Goals and Objectives Bank
- 279+ Free Speech Therapy Digital Materials
- 179+ Free Speech Therapy Wh-Questions Printable
